We’ve previously discussed granola, which Granola considered low FODMAP. Let’s now look at another topic, “Are green beans low FODMAP?”. Before that, we need to understand what determines whether a food is low FODMAP or high. This is important, so we can categorize foods into one of these categories.
What Makes a Food High or Low FODMAP?
Okay, let’s explain. FODMAPs are carbohydrates, specifically sugars and fiber, naturally occurring in food. These substances aren’t inherently good or bad, but for people with IBS, they can experience painful side effects. People with IBS who consume high FODMAPs may experience symptoms of gas, bloating, abdominal pain, and even diarrhea (constipation).
When discussing low FODMAP foods, Monash University is an important resource because they conduct research on foods containing FODMAPs. When trying to recover from IBS, foods high in FODMAPs should be avoided or limited. Therefore, it’s important to consume low-FODMAP foods. So, when you want to consume green beans, you might be wondering, “Are Green Beans low-FODMAP?”
It’s important to understand that low-FODMAP foods, if consumed in large quantities or exceeding the safe threshold, also provide a large supply of FODMAPs to the body and make it difficult for IBS sufferers to digest them, as these foods ferment in the intestines. This is what causes excessive gas, diarrhea, and other discomfort.
Why are Portions Important?
Portion size is crucial in a low-FODMAP diet. You may have experienced stomach upset when eating green beans one time, but not when consuming them another time. This is the difference between large portions and small portions. So, it’s all about portion size. Even low-FODMAP foods, even large portions, still contribute high-FODMAP substances.
To make it easier to understand low-FODMAP foods, we recommend using the Monash App. You can easily find specific foods and their recommended amounts.
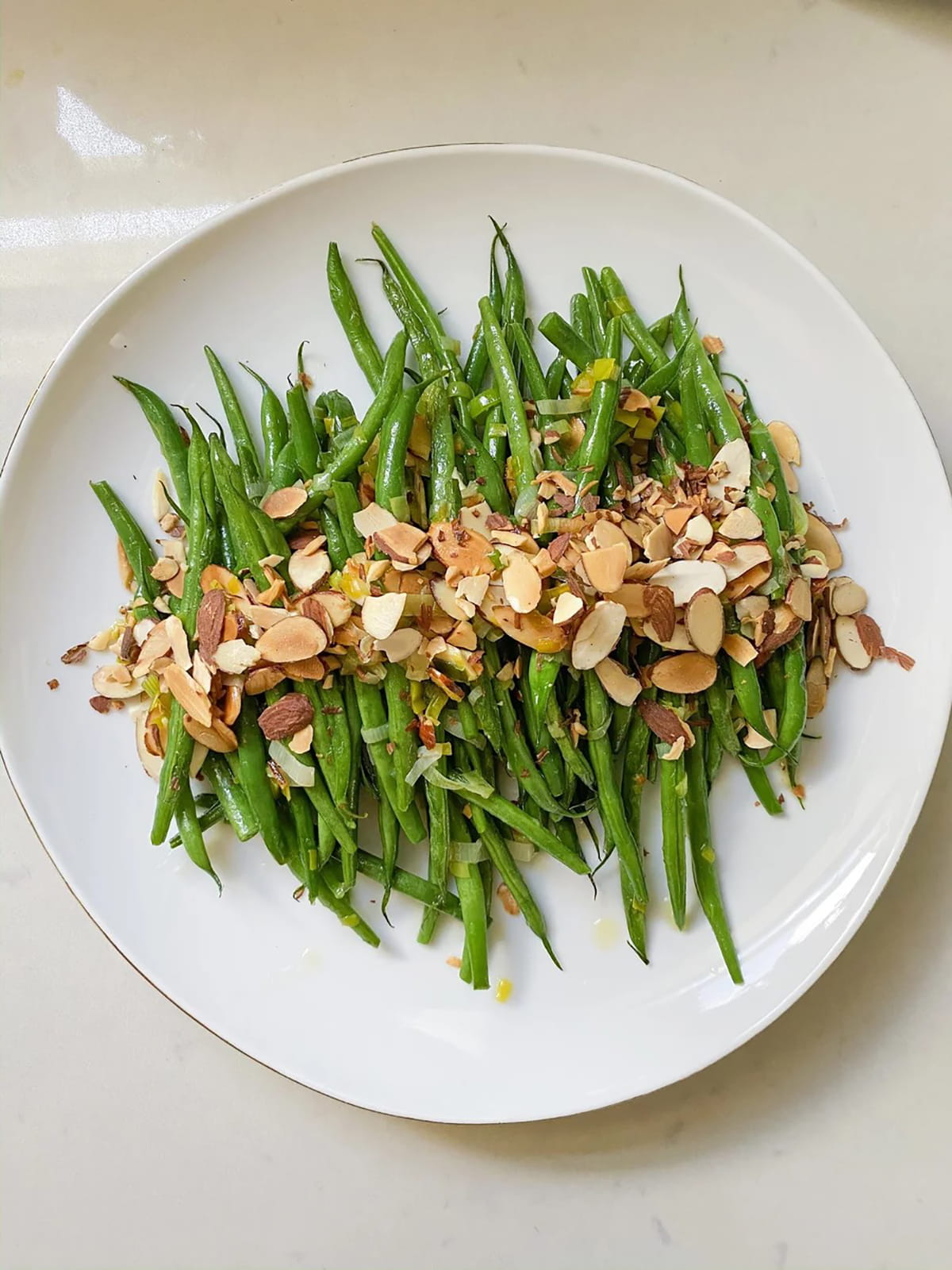
What about green bean portions? This is very easy to understand. The low-FODMAP limit is less than 1/2 cup (raw), which is for consumption during the elimination phase. If you already know your trigger foods, you can limit your green beans.
What FODMAPs Do Green Beans Contain?
Monash University experts tested green beans, but only on the raw (not canned) version. When cooked, green beans are considered low-FODMAP, so you can eat them cooked, fresh, frozen, or canned on a low-FODMAP diet.
So, what is it about green beans that makes them FODMAP? In a 1/2-cup serving (75g), green beans contain a moderate amount of sorbitol, a sugar alcohol.
If so, larger portions, such as 1 cup or 3/4 cup, are naturally higher in FODMAPs. In a 3/4-cup serving, green beans contain a high amount of sorbitol and moderate levels of mannitol. Different people have different tolerance levels.
If you are intolerant to sorbitol, you should limit your intake. However, if you’re intolerant to mannitol, there’s a greater degree of safety. You can consume more than those who are intolerant to sorbitol. The key is to adjust your portion size! A serving size between 1/2 and 3/4 cup is likely safe and tolerable for people with IBS.
Nutritional Benefits of Green Beans
What are the benefits of green beans that make many people concerned about them? They want to eat green beans, but on the other hand, they feel afraid of their digestive system.
Green beans are high in good fiber, contain a small amount of protein, and provide almost 10% of the daily folate requirement (vitamin B). In addition, green beans are also a source of several important minerals and vitamins such as calcium and vitamins C and A.
| Nutrient / Component | Amount / Note | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Fiber | High | – Supports healthy digestion – Helps control blood sugar – May reduce cholesterol levels |
| Protein | Small amount | – Contributes to muscle repair – Supports overall body function |
| Folate (Vitamin B9) | ~10% of daily requirement | – Essential for cell growth – Supports DNA synthesis – Helps prevent certain birth defects |
| Calcium | Present | – Supports strong bones and teeth – Aids muscle function |
| Vitamin C | Present | – Boosts immune system – Promotes collagen production – Acts as an antioxidant |
| Vitamin A | Present | – Supports vision – Promotes skin health – Strengthens immune function |
| Minerals (Iron, Potassium, etc.) | Present | – Iron helps prevent anemia – Potassium regulates blood pressure |
| Overall Benefits | — | – Promotes overall health and well-being – Supports strong immunity, healthy bones, and proper digestion – Helps maintain energy and prevent nutrient deficiencies |
How to use Green Beans in Your Low FODMAP Diet
- Use them as a side dish for dinner (protein, vegetables, green beans, rice, and chicken).
- They can also be enjoyed as a snack (eaten raw), stir-fried, roasted, mixed into soups, or added to salads.
Many low FODMAP recipes use green beans, including Low FODMAP Lemon Green Beans with Pine Nuts, Creamy Low FODMAP Green Bean Casserole, and many more.